Related Resources: Aerospace Design Engineering
Wind Turbine Blade Design
Applications and Design
Power Transmission and Technology
Wind Turbine Blade Design
Peter J. Schubel *
Richard J. Crossley
25 Pages
Minimum "Free" Membership Required to view document
Open: Wind Turbine Blade Design
Abstract: A detailed review of the current state-of-art for wind turbine blade design is presented, including theoretical maximum efficiency, propulsion, practical efficiency, HAWT blade design, and blade loads. The review provides a complete picture of wind turbine blade design and shows the dominance of modern turbines almost exclusive use of horizontal axis rotors. The aerodynamic design principles for a modern wind turbine blade are detailed, including blade plan shape/quantity, aerofoil selection and optimal attack angles. A detailed review of design loads on wind turbine blades is offered, describing aerodynamic, gravitational, centrifugal, gyroscopic and operational conditions.
Keywords: wind turbine; blade design; Betz limit; blade loads; aerodynamics
Introduction:
Power has been extracted from the wind over hundreds of years with historic designs, known as windmills, constructed from wood, cloth and stone for the purpose of pumping water or grinding corn. Historic designs, typically large, heavy and inefficient, were replaced in the 19th century by fossil fuel engines and the implementation of a nationally distributed power network. A greater understanding of aerodynamics and advances in materials, particularly polymers, has led to the return of wind energy extraction in the latter half of the 20th century. Wind power devices are now used to produce electricity, and commonly termed wind turbines.
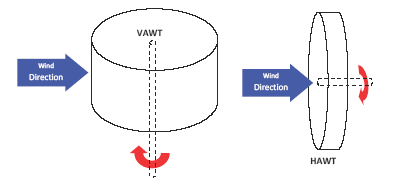
Alternative configurations for shaft and rotor orientation.
Related