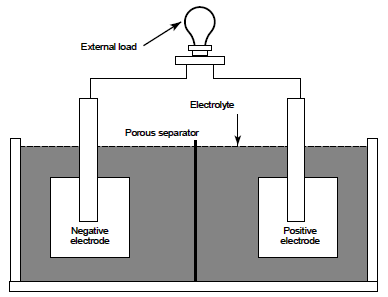
Simple Battery Components
Battery Application & Technology
The negative electrode supplies electrons to the external circuit (or load) during discharge. In a fully charged lead-acid storage battery the negative electrode is composed of sponge lead (Pb). The positive electrode accepts electrons from the load during discharge. In a fully charged lead-acid battery the positive electrode is composed of lead dioxide (PbO2 ). It should be noted that the electrodes in a battery must be of dissimilar materials or the cell will not be able to develop an electrical potential and thus conduct electrical current. The electrolyte completes the internal circuit in the battery by supplying ions to the positive and negative electrodes. Dilute sulfuric acid (H2 SO4 ) is the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries. In a fully charged lead-acid battery, the electrolyte is approximately 25% sulfuric acid and 75% water.
The separator is used to electrically isolate the positive and negative electrodes. If the electrodes are allowed to come in contact, the cell will short-circuit and become useless because both electrodes would be at the same potential. The type of separator used varies by cell type. Materials used as separators must allow ion transfer between the electrolyte and electrodes. Many separators are made of a porous plastic or glass fiber material. The above components are housed in a container commonly called a jar or container.