Electrochemistry of Lead Acid Battery Cell
Battery Application & Technology
All lead-acid batteries operate on the same fundamental reactions. As the battery discharges, the active materials in the electrodes (lead dioxide in the positive electrode and sponge lead in the negative electrode) react with sulfuric acid in the electrolyte to form lead sulfate and water. On recharge, the lead sulfate on both electrodes converts back to lead dioxide (positive) and sponge lead (negative), and the sulfate ions (SO42 ) are driven back into the electrolyte solution to form sulfuric acid. The reactions involved in the cell follow.
At the positive electrode:
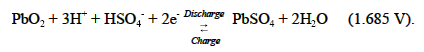
At the negative electrode:
![]()
Over cell:
![]()
Therefore the maximum open-circuit voltage that can be developed by a single lead-acid cell is 2.041 V.