Related Resources: calculators
Elongated Section Torque Applied Equation and Calculator
Beam Deflection and Stress Equation and Calculators
Torsion Applied Deformation and Stress of any elongated section with axis of symmetry OX; Equations and Calculator
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
Preview
Torsion Applied Deformation and Stress of any elongated section with axis of symmetry Calculator
![]()
Angle of Twist under applied Torque Moment
θ = ( T L ) / ( K G )
Shear Stress Maximum
For all solid sections of irregular form the maximum shear stress occurs at or very near one of the points where the largest inscribed circle touches the boundary,* and of these, at the one where the curvature of the boundary is algebraically least. (Convexity represents positive and concavity negative curvature of the boundary.) At a point where the curvature is positive (boundary of section straight or convex) this maximum stress is given approximately by:
![]()
Where:
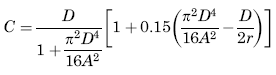
* Unless at some point on the boundary there is a sharp reentant angle, causing high local stress.
Where:
θ = angle of twist (radians),
α = degrees,
T = Twisting or torque moment force-length, (in-lbs, N-mm),
L = Length (in, mm),
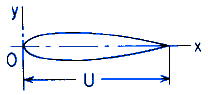
D = Diameter of largest inscribed circle (in, mm),
A = area of section (in2, mm2)
Ix = moment of inertia about axis of symmetry (in4, mm4),
U = Center Line Length (in, mm),
τ = Unit shear stress force / area (lbs/in2, N/mm2),
G = Modulus of rigidity force / area (lbs/in2, N/mm2),
K = Polar Moment of Inertia (in4, mm4) for section
Reference:
Roarks Formulas for Stress and Strain, 7th Edition, Table 10.1 Formulas for torsional deformation and stress.