Related Resources: calculators
Load Uniformly Decreasing Equation and Calculator
Flat Rectangular Plate, Two Edges Fixed, Two Edges Free Load Uniformly Decreasing from z = 0 to z = (2/3) b Equation and Calculator.
Per. Roarks Formulas for Stress and Strain for flat plates with straight boundaries and constant thickness
Flat Rectangular plate, Two Edges Fixed, Two Edges Free Load Uniformly Decreasing from z = 0 to z = (2/3) b.
|
Rectangular plate;
Two Edges Fixed Two Edges Free 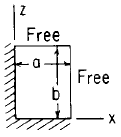 |
Load Uniformly
Decreasing from z = 0 to z = (2/3) b |
At x = 0, z = 0
Stress and Reaction Force
![]()
Reaction Force
![]()
Stress and Reaction Force at x = 0, z = 0.4b if a ≥ 0.375b, or Z = 0.2b if a < 0.375b
![]()
Reaction Force
![]()
Where used:
E = Modulus of Elasticity (lbs/in2)
q = Total load or force to Plate (lbs/in2)
v = Poisson’s ratio (assumed to be 0.3)
t = plate thickness, (in)
a = plate length, (in)
b = plate width, (in)
σb = stress, (lbs/in2)
R = Reaction Force (lbs/in)
β1,2 = Constant From Table A
γ1,2 = Constant From Table A
Table A
|
a/b
|
.125
|
0.25
|
0.375
|
0.5
|
0.75
|
1.0
|
|
β1
|
0.040
|
0.109
|
0.154
|
0.215
|
0.304
|
0.362
|
|
β2
|
0.026
|
0.059
|
0.089
|
0.107
|
0.116
|
0.113
|
|
γ1
|
0.250
|
0.354
|
0.316
|
0.338
|
0.357
|
0.357
|
|
γ2
|
0.084
|
0.129
|
0.135
|
0.151
|
0.156
|
0.152
|
Reference:
Roarks Formulas for Stress and Strain, 7th Edition