Related Resources: calculators
Plate Loading Uniformly Decreasing from Fixed Edge to Zero at 2/3 b Stress and Deflection Equation and Calculator
Flat Rectangular Plate; one edge fixed, opposite edge free, remaining edges simply supported loading Uniformly decreasing from fixed edge to zero at 2/3 b Stress and Deflection Equation and Calculator.
Per. Roarks Formulas for Stress and Strain Formulas for flat plates with straight boundaries and constant thickness
Rectangular plate; one edge fixed, opposite edge free, remaining edges simply supported loading Uniformly decreasing from fixed edge to zero at 2/3 b.
|
Rectangular plate; one edge fixed,
opposite edge free, remaining edges simply supported. 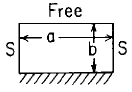 |
Uniformly decreasing
from fixed edge to zero at 2/3 b. |
Stress Maximum at center of fixed edge:
| and | R = γqb |
Symbols used:
q = Applied Load or Force to Flat Area of Plate (N/m2, lbs/2)
v = Poisson’s ratio (assumed to be 0.2)
t = plate thickness, (m, in)
a = plate length, (m, in)
b = plate width, (m, in)
σ = stress, (N/m2, lbs/in2)
R = Reaction force per unit length (N/m, lbs/in) normal to the plate surface exerted by the boundary support on the edge of the plate.
β = Constant From Table A
γ = Constant From Table A
Table A
|
a/b
|
0.25
|
0.50
|
0.75
|
1.0
|
1.5
|
2.0
|
3.0
|
|
β
|
0.033
|
0.094
|
0.146
|
0.200
|
0.272
|
0.339
|
0.400
|
|
γ
|
0.148
|
0.233
|
0.277
|
0.304
|
0.330
|
0.339
|
0.340
|
Reference:
Roarks Formulas for Stress and Strain, 7th Edition