USB Cables / Interface Overview
Computer Technology Engineering Menu
 |
|---|
USB Cables / Interface overview - USB 2.0, occasionally referred to as Hi-Speed USB, is the next generation Universal Serial Bus interface technology (used in computer and consumer electronics industries and applications) that allows for the connection of multiple components (such as keyboards, CD-ROM drives, network hubs, joysticks, mice, printers and more) to a PC or laptop computer. Additionally, a wide range of peripheral components such as CD burners, web cams, digital cameras, scanners, printers, hubs, speakers, and PDAs (personal digital assistants) have integrated USB 2.0 technology. USB 2.0 allows for transfer of data at a rate 40 times faster than the original USB standard � in fact, the rate of transfer can be as high as 480 MBps (Mega Bits per second) when evaluated against USB 1.1 products, which typically has a transfer rate of 1.1 MBps. Additionally, by adding hubs, USB 2.0 allows for the connection of up to 127 devices to one computer.
 |
|---|
Electronic devices which attach to the USB bus may belong to a industry standard device class. Depending on how the device class has been set for the electronics device will determine the class number assigned. If the class is set for the entire device, the number assigned is the bDeviceClass field of the device descriptor, and if it is to be set for a single interface on a device, it is assigned to the bInterfaceClass field of the interface descriptor.
The most used device classes (grouped by assigned class ID) are:
0x00 - Reserved value - used in the device descriptor to signify that the interface descriptor holds the device class identifier for each interface.
0x01 USB audio device class , sound card -like devices. 0x03 USB human interface device class ("HID"), keyboards, mice, etc.
0x06 Still image capture device class, identical to the Picture Transfer Protocol as used across USB 0x07 USB printer device class , printer -like devices.
0x08 USB mass storage device class used for flash drives , portable hard drives, memory card readers, digital cameras, digital audio players etc. This device class presents the device as a block device (almost always used to store a file system ).
0x09 USB hubs .
0x0A USB communications device class used for modems , network cards , ISDN connections, Fax .
0x0E USB video device class , webcam -like devices, motion image capture devices.
0xE0 Wireless controllers, for example Bluetooth dongles.
0xFF Custom device class - used to establish that a device or interface does not support any standard device class and requires custom drivers
USB Cable Construction:
USB cables are contructed using 20 or 28 AWG wire, using the colors Black, Red, Green, and White (see Standard USB Pin Signaling Chart below). The signal wires, D+ and D- are twisted pairs. The four wires, Potential, Ground and Signal wires are contained within foil, and then a braid along with a drain wire. The entire cable is then enclosed within a rugged protecting synthetic non-conducting tubular coat.
 |
|---|
Standard USB Pin Signaling
Pinout |
Host |
Device |
|
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Red |
Vbus 4.75 - 5.25 V |
Vbus 4.4 - 5.25 V |
2 |
White |
D - |
D - |
3 |
Green |
D + |
D + |
4 |
Black |
Ground |
Ground |
USB Pin-Outs
|
|
USB Standard "B" |
|
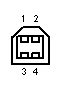 |
|
 |
 |
USB Standard "A" |
|
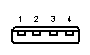 |
|
 |
 |