Equivalent Piping Length Head Loss Equation Fluids
Fluid Flow Table of Contents
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Knowledge
Equivalent Piping Length Head Loss Equation Fluids
Minor losses may be expressed in terms of the equivalent length (Leq) of pipe that would have the same head loss for the same discharge flow rate. This relationship can be found by setting the two forms of Darcys equation equal to each other.
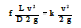
This yields two relationships that are useful.

Typical values of Leq/D for common piping system components are listed in Table 1. The equivalent length of piping that will cause the same head loss as a particular component can be determined by multiplying the value of Leq/D for that component by the diameter of the pipe. The higher the value of Leq/D, the longer the equivalent length of pipe.
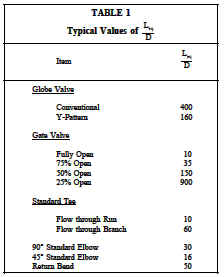
Example:
A fully-open gate valve is in a pipe with a diameter of 10 inches. What equivalent length of pipe would cause the same head loss as the gate valve?
Solution:
From Table 1, we find that the value of Leq/D for a fully-open gate valve is 10.
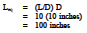
By adding the equivalent lengths of all components to the actual length of pipe in a system we can obtain the Leq value for the entire piping system.