Pump System Operating Point Review
Fluid Flow Table of Contents
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Knowledge
The point at which a pump operates in a given piping system depends on the flow rate and head loss of that system. For a given system, volumetric flow rate is compared to system head loss on a system characteristic curve. By graphing a system characteristic curve and the pump characteristic curve on the same coordinate system, the point at which the pump must operate is identified. For example, in Figure 10, the operating point for the centrifugal pump in the original system is designated by the intersection of the pump curve and the system curve (hLo).
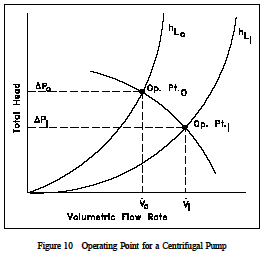
The system has a flow rate equal to and a total system head loss equal to DPo. In order to ˙Vo maintain the flow rate , the pump head must be equal to DPo. In the system described by ( ˙Vo) the system curve (hL1), a valve has been opened in the system to reduce the systems resistance to flow. For this system, the pump maintains a large flow rate at a smaller pump head ( ˙V1) (DP1).