Conduction - Rectangular Coordinates - Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer Engineering | Thermodynamics
Heat conduction is a phenomenon that occurs through the interaction of neighbouring atoms and molecules, transferring their energy/heat (partially) to their neighbours. This is the most significant means of heat transfer within a solid and between solid objects in thermal contact.
For the following example, see Conduction - Heat transfer.
Example:
1000 Btu/hr is conducted through a section of insulating material shown in Figure 1 that measures 1 ft2 in cross-sectional area. The thickness is 1 in. and the thermal conductivity is 0.12 Btu/hr-ft-F. Compute the temperature difference across the material.
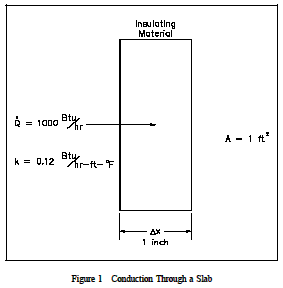
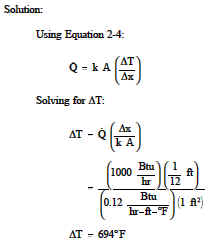
Example:
A concrete floor with a conductivity of 0.8 Btu/hr-ft-F measures 30 ft by 40 ft with a thickness of 4 inches. The floor has a surface temperature of 70F and the temperature beneath it is 60F. What is the heat flux and the heat transfer rate through the floor?

