Related Resources: heat transfer
Heat Loss from Ducts Equations and Calculator
Heat Transfer Engineering
Thermodynamics
Engineering Physics
Heat Loss from Ducts in a Building Equation and Calculator and cost of energy lost.
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
Preview: Heat Loss from Ducts in a Building Equation and Calculator
![]()
Where:
Q = Rate of heat transfer
m = mass flow rate
Cp = Specific heat at constant pressure
ΔT = Change of temperature
![]()
Where:
p = Density
P = Abosolute pressure
R = Gas constant
T = Absolute temperature
![]()
m = Mass flow rate
p = Density
Ac = Area
V = Average fluid velocity
Example:
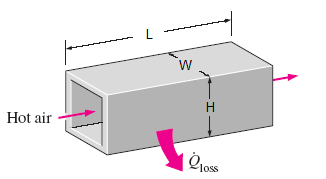
Heat Loss from Heating Ducts in a Basement:
A 5-m-long section of an air heating system of a house passes through an unheated space in the basement (see figure above). The cross section of the rectangular duct of the heating system is 20 cm x 25 cm. Hot air enters the duct at 100 kPa and 60°C at an average velocity of 5 m/s. The temperature of the air in the duct drops to 54°C as a result of heat loss to the cool space in the basement.
Determine the rate of heat loss from the air in the duct to the basement under steady conditions. Also, determine the cost of this heat loss per hour if the house is heated by a natural gas furnace that has an efficiency of 80 percent, and the cost of the natural gas in that area is $0.60/therm (1 therm = 100,000 Btu = 105,500 kJ).
Solution: The temperature of the air in the heating duct of a house drops as a result of heat loss to the cool space in the basement. The rate of heat loss from the hot air and its cost are to be determined.
Assumptions
1 Steady operating conditions exist.
2 Air can be treated as an ideal gas with constant properties at room temperature.
Properties The constant pressure specific heat of air at the average temperature of (54°C + 60°C)/2 = 57°C is 1.007 kJ/kg · °C See (Properties of air at 1 atm pressure).
Analysis We take the basement section of the heating system as our system, which is a steady-flow system.
![]()
The cross-sectional area of the duct is:
![]()
Then the mass flow rate of air through the duct and the rate of heat loss become
![]()
therefore,

or 5688 kJ/h. The cost of this heat loss to the home owner is
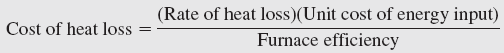
Conversion: 1 Therm = 105,480 kJ
Conclusion:
The heat loss from the heating ducts in the basement is costing the home owner 4 cents per hour. Assuming the heater operates 2000 hours during a heating season, the annual cost of this heat loss adds up to $80. Most of this money can be saved by insulating the heating ducts in the unheated areas.