Related Resources: heat transfer
Heat Loss Insulated Electric Wire Equations and Calculator
Heat Transfer Engineering
Thermodynamics
Engineering Physics
Heat Loss From an Insulated Electric Wire Equation and Calculator:
Assumptions:
1 Heat transfer is steady since there is no indication of any change with time.
2 Heat transfer is one-dimensional since there is thermal symmetry about the centerline and no variation in the axial direction.
3 Thermal conductivities are constant.
4 The thermal contact resistance at the interface is negligible.
5 Heat transfer coefficient incorporates the radiation effects, if any.
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
Preview: Heat Loss From an Insulated Electric Wire Calculator
![]()
Area of wire
![]()
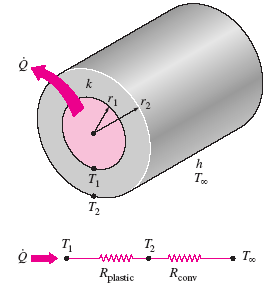
Conduction resistance for the plastic cover and a convection resistance for the outer surface in series
![]()
![]()
Total Conduction Resistance
![]()
Interface temperature
![]()
Critical radius of insulation of the plastic cover.
![]()
Where:
Q = Heat Steady State Transfer (W)
A = Area (m2)
L = Length (m)
V = Voltage (v)
I = Amperage (amps)
rn = Radius (m)
k = Thermal Conductivity (W/m · °C)
T∞n = Temperature (°C)
Tn = Temperature (°C)
hn = Heat Transfer Coefficient (W/m2 · °C)
Rconv = Thermal Resistance (°C/W)
Rplastic = Thermal Resistance Glass (°C/W)