Related Resources: heat transfer
Heat Loss Through Wall Equation and Calculator
Heat Transfer Engineering
Thermodynamics
Engineering Physics
Heat Loss Through a Wall Equation and Calculator
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
Preview: Heat Loss Through a Wall Calculator
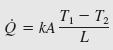
or
![]()
Where:
Q = Heat Steady State Transfer (W)
T1 = Temperature (°C)
T2 = Temperature (°C)
k = Thermal Conductivity (W/m · °C)
ΔTwall = Change in temperature (°C)
Rwall = Junction thermal resisitance (°C/W)
Example:
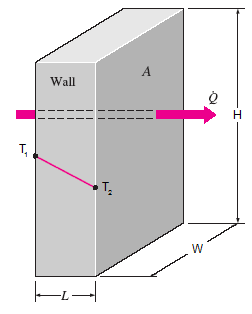
Consider a 3-m-high, 5-m-wide, and 0.3-m-thick wall whose thermal conductivity is k = 0.9 W/m · °C . On a certain day, the temperatures of the inner and the outer surfaces of the wall are measured to be 16°C and 2°C, respectively. The rate of heat loss through the wall on that day.
The two surfaces of a wall are maintained at specified temperatures. The rate of heat loss through the wall is to be determined.
Assumptions
1 Heat transfer through the wall is steady since the surface temperatures remain constant at the specified values.
2 Heat transfer is one dimensional since any significant temperature gradients will exist in the direction from the indoors to the outdoors.
3 Thermal conductivity is constant.
![]()
Alternativeliy the steady rate of heat transfer through the wall by making use of the thermal resistance concept from
![]()
Where:
![]()
Substituting
![]()