Related Resources: heat transfer
Maximum Power Dissipation Transistor Equations and Calculator
Heat Transfer Engineering
Thermodynamics
Engineering Physics
Maximum Power Dissipation of a Transistor Equation and Calculator:
Assumptions:
1 Steady operating conditions exist.
2 The transistor case is isothermal at 85°C.
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
Preview: Maximum Power Dissipation of a Transistor Calculator
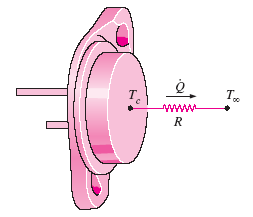
Rate of heat transfer
![]()
Where:
Q = Heat Steady State Transfer (W)
Rcase-ambient = Rated case-to-ambient thermal resistance (°C/W)
Tc = Transistor case temperature (°C)
T∞ = Surrounding environment temperature (°C)
The transistor can be used at higher power levels by attaching it to a heat sink (which lowers the thermal resistance by increasing the heat transfer surface area, as discussed in the next example) or by using a fan (which lowers the thermal resistance by increasing the convection heat transfer coefficient).