Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Inspection Method (NDI)
Quality and Inspection Process Knowledge
Ultrasonic inspection is an NDI technique that uses sound energy moving through the test specimen to detect flaws. The sound energy passing through the specimen will be displayed on a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) computer data program, or video/camera medium. Indications of the front and back surface and internal/external conditions will appear as vertical signals on the CRT screen or nodes of data in the computer test program. There are three types of display patterns; A scan, B scan, and C scan. Each scan provides a different picture or view of the specimen being tested.
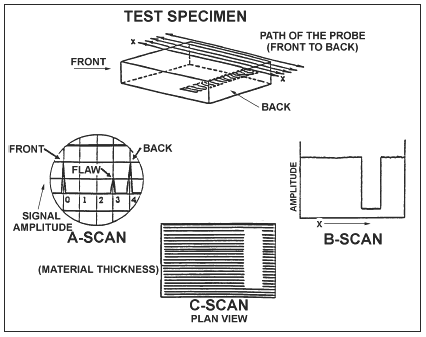
The amount of reflection that occurs when a sound wave strikes an interface depends largely on the physical state of the materials forming the interface and to a lesser extent on the specific physical properties of the material. For example: sound waves are almost completely reflected at metal/gas interfaces; and partial reflection occurs at metal/liquid or metal/solid interfaces.