Related Resources: instrumentation
Pressure Tube Anemometer Measurement Equation
Power Transmission and Technology Menu
Applications and Design
Pressure Tube Anemometer Air Flow Measurement Equation
The tube anemometer which uses the air flow pressure to measure the velocity. This works on the principle that, the air flow passing through the tube creates pressure where as the flow across a tube results in suction. Consider two tubes as shown in the Fig. 1 The pressure in the tube
parallel to the wind is the sum of atmospheric pressure and the wind pressure.
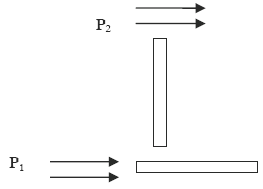
Tube Anemometer Figure 1
Eq. 1
P1 = PA + 0.5 · C1 · ρ a · V2
Similarly in the tube perpendicular to the wind, the pressure is
Eq. 2
P2 = PA - 0.5 · C2 · ρ a · V2
where PA is the atmospheric pressure and C1 and C2 are coefficients. Subtracting P2 from P1 and solving for V, we get
Eq. 3
V = [ 2 ( P1 - P2 ) / ( ρ a · ( C1 + C2 ) ) ]0.5
Thus, by measuring the difference in pressure inside the two tubes, the wind velocity can be estimated. Values of C1 and C2 are available with the instrument. The pressure is measured using standard manometers or pressure transducers. The major advantage of pressure tube anemometer is that it does not have any moving parts. This anemometer has limited application in the open field measurements as the presence of dust, moisture and insects can affect its accuracy.
Related:
- Cup Anemometer Wind Measurement Formulae and Calculator
- Hot-Wire Anemometer Flow Detector Review
- Wind Turbine Power and Torque Equation and Calculator
- Wind Turbine Power From Wind
- Wind Power Generation and Wind Power Turbine Design
- Aerodynamics of Wind Turbine
- Wind Energy Fundamentals
- Wind Energy, Renewable Energy and the Environment
- Hydraulic Turbine Power Formulae and Calculator
Source:
Sathyajith Mathew
Wind Energy Fundamentals, Resource Analysis and Economics