Five Axis CNC Machining Basics
About Five Axis CNC Machining Basics
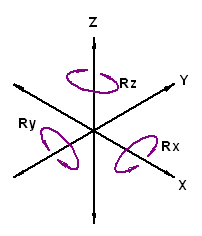
Five axis CNC machining refers to the ability of the CNC machine to perform movement about five different axis simultaneously. Most CNC manufacturers define their machines movement starting with the three primary axis, X. Y and Z, with the Z axis being parallel to the tool spindle, see Figure 1. The other two axis are given by the machines ability to rotate about the X and Y axis. Axis Rx pivots or rotates parallel and about the X axis. Axis Ry pivots or rotates parallel to and about the Y axis. Axis Rz is represents the rotation of the cutting tool installed into the machine spindle center.
 |
|---|
The benefits of five-axis machining is the machines ability to machine complex shapes in a single set-up. This reduces the machinist setup time and increases production rates . By eliminating multiple set-ups, time and errors are reduced. Additionally, the feature-to-features accuracy is improved because the same zero or datum reference frame is used throughout the manufacturing process. Other advantages of five axis machining is the since simultaneous movement is allowed along the X and Y axis, shorter and more rigid tools may be used. Also, higher spindle/cutting tool speeds may be achieved while reducing the load on the cutting tool.
Shorter and thicker cutters also reduce vibration when machining deep pockets or contoured features with three-axis machines. Example applications for five axis CNC machining are complex three dimensional profiles. These geometric are common for impellars, turbine blades, and plastic mold tools.