Disk Brake Design Equations and Calculator
Mechanics and Machines Calculations Menu
Disk Brake Design Equations
The disc brake is a wheel brake which slows rotation of the wheel by the friction caused by pushing brake pads against a brake disc with a set of calipers. The brake disc (or rotor in American English) is usually made of cast iron, but may in some cases be made of composites such as reinforced carbon–carbon or ceramic matrix composites. This is connected to the wheel and/or the axle.
To stop the wheel, friction material in the form of brake pads, mounted on a device called a brake caliper, is forced mechanically, hydraulically, pneumatically or electro magnetically against both sides of the disc. Friction causes the disc and attached wheel to slow or stop. Brakes convert motion to heat, and if the brakes get too hot, they become less effective, a phenomenon known as brake fade.
Open: Advanced Disk and Shoe Brake Design Calculator
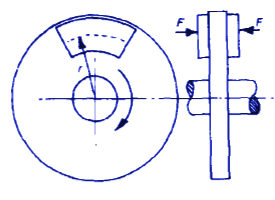
Let:
F = force on pad
r = mean radius of pad
A = pad area
Torque capacity (2 pads):
![]()
Pad pressure:
p = F/A