Related Resources: pressure-vessel
Dished Head Formula hemispherical, elliptical ASME Pressure Vessel Section I Equations and
ASME Pressure Vessel Design and Engineering
ASME Pressure Vessel Section I: Dished Head Formulae Equations and Calculator:
The ASME Section VIII – Division 1 determines the rules for dished heads. The most common configurations are spherical, hemispherical, elliptical (or ellipsoidal) and torispherical shapes. How the shapes are, make some confusion for beginners and even professionals users of ASME Section VIII. To cast a little light on these subjects see below:
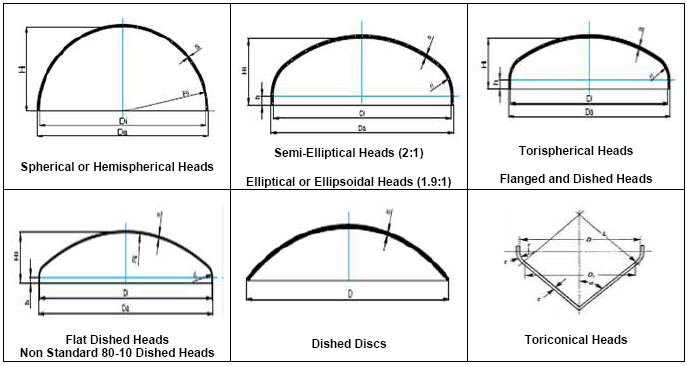
Spherical or Hemispherical Heads:
When t < 0.356R or P < 0.665SE - (Thin Spherical or Hemispherical Heads):
![]()
or
![]()
Preview ASME Pressure Vessel Section I: Full-Hemispherical Head Calculator
Where:
t = Minimum thickness of head (in);
P = maximum allowable working pressure (psi);
R = Radius to which the head was formed (in);
E = Weld Joint efficiency
S = Maximum Allowable Working Stress (psi). According to ASME Section II, Table 1A.
Example:
Thin Spherical or Hemispherical Head:
A pressure vessel is built of SA-516-70 material and has an inside diameter of 96 in. The internal design pressure is 100 psi at 450°F. Corrosion allowance is 0.125 in. and joint efficiency is E = 0.85. Calculate the required spherical head thickness of the pressure vessel if “S” is 20,000 psi?
Since P > 0.665SE = P > 11,305 psi. Thus, as 11,305 > 100 psi.
The inside radius in a corroded condition is equal to, R = 48 + 0.125 = 48.125 in.
t = ( 100 x 48.125 ) / ( 2 * 20,000 * 0.85 - 0.2 * 100 )
t = 0.142