Related Resources: thermodynamics
Van der Waals Constants for Gases
Engineering Materials Specifications and Characteristics Tables and Charts
Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
Van der Waals Constants for Gases
Van der Waals, constant a is due to force of attraction and b due to the infinite size molecules. The greater the value q and smaller the value b, larger the liquefaction.
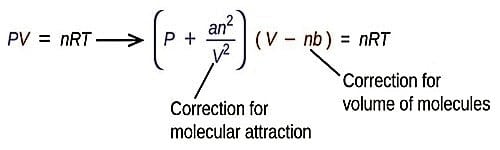
The formula for Van der Waals equation of state for a real gas is:
(P + n2a/V2)(V -nb) = nRT
where:
P is the pressure,
V the volume,
T the temperature,
n the amount of substance (in moles),
R the gas constant.
The van der Waals constants a and b are characteristic of the substance and are independent of temperature. They are related to the critical temperature and pressure, Tc and Pc, by
a = 27R2Tc2/64Pcb = RTc /8Pc
This table gives values of a and b for some common gases. Most of the values have been calculated from the critical temperature and pressure values given in the table “Critical Constants” in this section. Van der Waals constants for other gases may easily be calculated from the data in that table.
To convert the van der Waals constants to SI units, note that 1 bar L2/mol2 = 0.1 Pa m6/mol2 and 1 L/mol = 0.001 m3/mol.
Substance |
a |
b |
bar L2/mol2 |
L/mol |
|
Acetic acid |
17.71 |
0.1065 |
Acetone |
16.02 |
0.1124 |
Acetylene |
4.516 |
0.0522 |
Ammonia |
4.225 |
0.0371 |
Aniline |
29.14 |
0.1486 |
Argon |
1.355 |
0.0320 |
Benzene |
18.82 |
0.1193 |
Bromine |
9.75 |
0.0591 |
Butane |
13.89 |
0.1164 |
1-Butanol |
20.94 |
0.1326 |
2-Butanone |
19.97 |
0.1326 |
Carbon dioxide |
3.658 |
0.0429 |
Carbon disulfide |
11.25 |
0.0726 |
Carbon monoxide |
1.472 |
0.0395 |
Chlorine |
6.343 |
0.0542 |
Chlorobenzene |
25.80 |
0.1454 |
Chloroethane |
11.66 |
0.0903 |
Chloromethane |
7.566 |
0.0648 |
Cyclohexane |
21.92 |
0.1411 |
Cyclopropane |
8.34 |
0.0747 |
Decane |
52.74 |
0.3043 |
1-Decanol |
59.51 |
0.3086 |
Diethyl ether |
17.46 |
0.1333 |
Dimethyl ether |
8.690 |
0.0774 |
Dodecane |
69.38 |
0.3758 |
1-Dodecanol |
75.70 |
0.3750 |
Ethane |
5.580 |
0.0651 |
Ethanol |
12.56 |
0.0871 |
Ethylene |
4.612 |
0.0582 |
Fluorine |
1.171 |
0.0290 |
Furan |
12.74 |
0.0926 |
Helium |
0.0346 |
0.0238 |
Heptane |
31.06 |
0.2049 |
1-Heptanol |
38.17 |
0.2150 |
Hexane |
24.84 |
0.1744 |
1-Hexanol |
31.79 |
0.1856 |
Hydrazine |
8.46 |
0.0462 |
Hydrogen |
0.2452 |
0.0265 |
Hydrogen bromide |
4.500 |
0.0442 |
Hydrogen chloride |
3.700 |
0.0406 |
Hydrogen cyanide |
11.29 |
0.0881 |
Hydrogen fluoride |
9.565 |
0.0739 |
Hydrogen iodide |
6.309 |
0.0530 |
Substance |
a |
b |
bar L2/mol2 |
L/mol |
|
Hydrogen sulfide |
4.544 |
0.0434 |
Isobutane |
13.32 |
0.1164 |
Krypton |
5.193 |
0.0106 |
Methane |
2.303 |
0.0431 |
Methanol |
9.476 |
0.0659 |
Methylamine |
7.106 |
0.0588 |
Neon |
0.208 |
0.0167 |
Neopentane |
17.17 |
0.1411 |
Nitric oxide |
1.46 |
0.0289 |
Nitrogen |
1.370 |
0.0387 |
Nitrogen dioxide |
5.36 |
0.0443 |
Nitrogen trifluoride |
3.58 |
0.0545 |
Nitrous oxide |
3.852 |
0.0444 |
Octane |
37.88 |
0.2374 |
1-Octanol |
44.71 |
0.2442 |
Oxygen |
1.382 |
0.0319 |
Ozone |
3.570 |
0.0487 |
Pentane |
19.09 |
0.1449 |
1-Pentanol |
25.88 |
0.1568 |
Phenol |
22.93 |
0.1177 |
Propane |
9.39 |
0.0905 |
1-Propanol |
16.26 |
0.1079 |
2-Propanol |
15.82 |
0.1109 |
Propene |
8.442 |
0.0824 |
Pyridine |
19.77 |
0.1137 |
Pyrrole |
18.82 |
0.1049 |
Silane |
4.38 |
0.0579 |
Sulfur dioxide |
6.865 |
0.0568 |
Sulfur hexafluoride |
7.857 |
0.0879 |
Tetrachloromethane |
20.01 |
0.1281 |
Tetrachlorosilane |
20.96 |
0.1470 |
Tetrafluoroethylene |
6.954 |
0.0809 |
Tetrafluoromethane |
4.040 |
0.0633 |
Tetrafluorosilane |
5.259 |
0.0724 |
Tetrahydrofuran |
16.39 |
0.1082 |
Thiophene |
17.21 |
0.1058 |
Toluene |
24.86 |
0.1497 |
1,1,1-Trichloroethane |
20.15 |
0.1317 |
Trichloromethane |
15.34 |
0.1019 |
Trifluoromethane |
5.378 |
0.0640 |
Trimethylamine |
13.37 |
0.1101 |
Water |
5.537 |
0.0305 |
Xenon |
4.192 |
0.0516 |
Reference:
Reid, R.C, Prausnitz, J. M., and Poling, B.E., The Properties of Gases and Liquids, Fourth Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1987.