Related Resources: calculators
Total Head Pressure Velocity Equations and Calculator
Hydraulic & Pneumatic Design Engineering
Fluids Flow Design and Engineering
Total Head Pressure and Velocity Equation and Calculator
Energy in an Incompressible Liquid
An incompressible liquid can have energy in the form of velocity, pressure, or elevation.
Preview Total Head Pressure & Velocity Calculator (Premium Membership required for calculator)
Liquid flowing in a conduit can undergo changes in energy form. Bernoulli’s theorem for an incompressible liquid states that in steady flow, without losses, the energy at any point in the conduit is the sum of the velocity head, pressure head, and elevation head and that this sum is constant along a streamline in the conduit. Therefore, the energy at any point in the system relative to a selected datum plane is
Total Head Pressure
Eq. 1
Velocity Head Pressure
Eq. 2
Where
H = energy (total head) of system, ft · lb/lb or ft (N · m/N or m)
V = velocity, ft/s (m/s)
g = acceleration of gravity, 32.17 ft/s2 (9.807 m/s2)
p = pressure, lb/ft2 (N/m2)
γ = specific weight (force) of liquid, lb/ft3 (N/m3)
Z = elevation above (+) or below (-) datum plane, ft (m)
Figure 1, Velocity Head, Equivalent Velocity Head
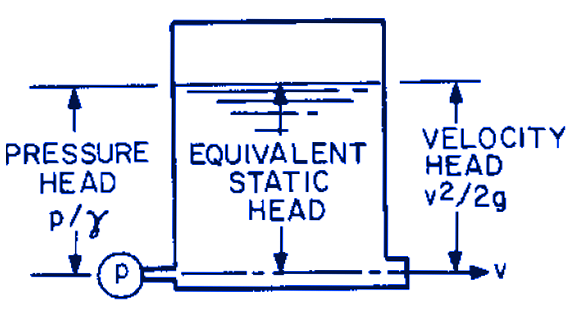
The velocity and pressure at the point of energy measurement are expressed in units of equivalent head and are added to the distance Z that this point is above or below the selected datum plane. If pressure is measured as gage (relative to atmosphere), total head H is gage; if pressure is measured as absolute, total head H is absolute. Equation 1 can also be applied to liquid at rest in a vertical column or in a large vessel (or to liquids of various densities) to account for changes in pressure with changes in elevation or vice versa. The equivalent of velocity and pressure energy heads in feet (meters) can be thought of as the height to which a vessel of liquid of constant density has to be filled, above the point of measurement, to create this same velocity or pressure.
Related:
- Head Changes Caused by Pipe Size Enlargement Formula and Calculator
- Head Changes Caused by Pipe Size Sudden Reduction Formula and Calculator
- Head Loss at Pipe Entrance Equations and Calculator using the head loss coefficient and head loss of a fluid at a smooth bellmouth pipe entrance.
- Head Loss at Pipe Abrupt Exit Equations and Calculator of a fluid.
- Head loss and head loss coefficient equation and calculator of a fluid in across a screen (circular metal wire mesh) inside a pipe.
- Head coefficient and head loss across angled louvers inside a pipe equation and calculator.
- Extended Bernoulli Bernoulli equation can be modified to take into account gains and losses of head.
- Net Positive Suction Head Centrifugal pumps generally obey what are known as the pump laws.
- System Head Characteristic Curve Head Loss Piping System Review | Head Loss Curve
- System Operating Point The point at which a pump operates in a given piping system depends on the flow rate and head loss of that system.
- Velocity of Water Due To Head in Feet Table
- Centrifugal Pumps in Parallel If the inlet and the outlet of each pump are at identical points in the system, each pump must produce the same pump head.
- Centrifugal Pumps in Series Centrifugal pumps are used in series to overcome a larger system head loss than one pump can compensate for individually.
- Pipe Diameter Based on & Friction Factor Calculator Calculator will determine pipe diameter required based on Head Loss, hL, Frictional Pressure Drop, DPf, for given flow rate, Q, pipe diameter, D, pipe length, L, pipe roughness, e, and fluid properties, r & m.
- Pipe Flow Rate Based on & Friction Factor Calculator Calculator will determine pipe diameter required based on Head Loss, hL, Frictional Pressure Drop, DPf, for given flow rate, Q, pipe diameter, D, pipe length, L, pipe roughness, e, and fluid properties, r & m.
- Pipe Friction Head Loss, Friction Pressure, and Frictional Pressure Equations and Calculator Pipe Friction Head Loss, Friction Pressure, and Frictional Pressure Equations and Calculator
- Head Loss Head loss is the reduction in the total head or pressure of the fluid as it moves through a fluid system.
- Equivalent Piping Length Equivalent Piping Length Head Loss Equation Fluids
Reference:
Pressure Design Manual, Third Edition, Dennis Moss 2004